Welding Fire Blankets: Essential Protection for Hot Work Safety
Welding fire blankets are crucial safety tools that protect against sparks, molten metal, and accidental fires during welding operations. This guide explains their materials, proper usage, maintenance, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What Are Welding Fire Blankets?
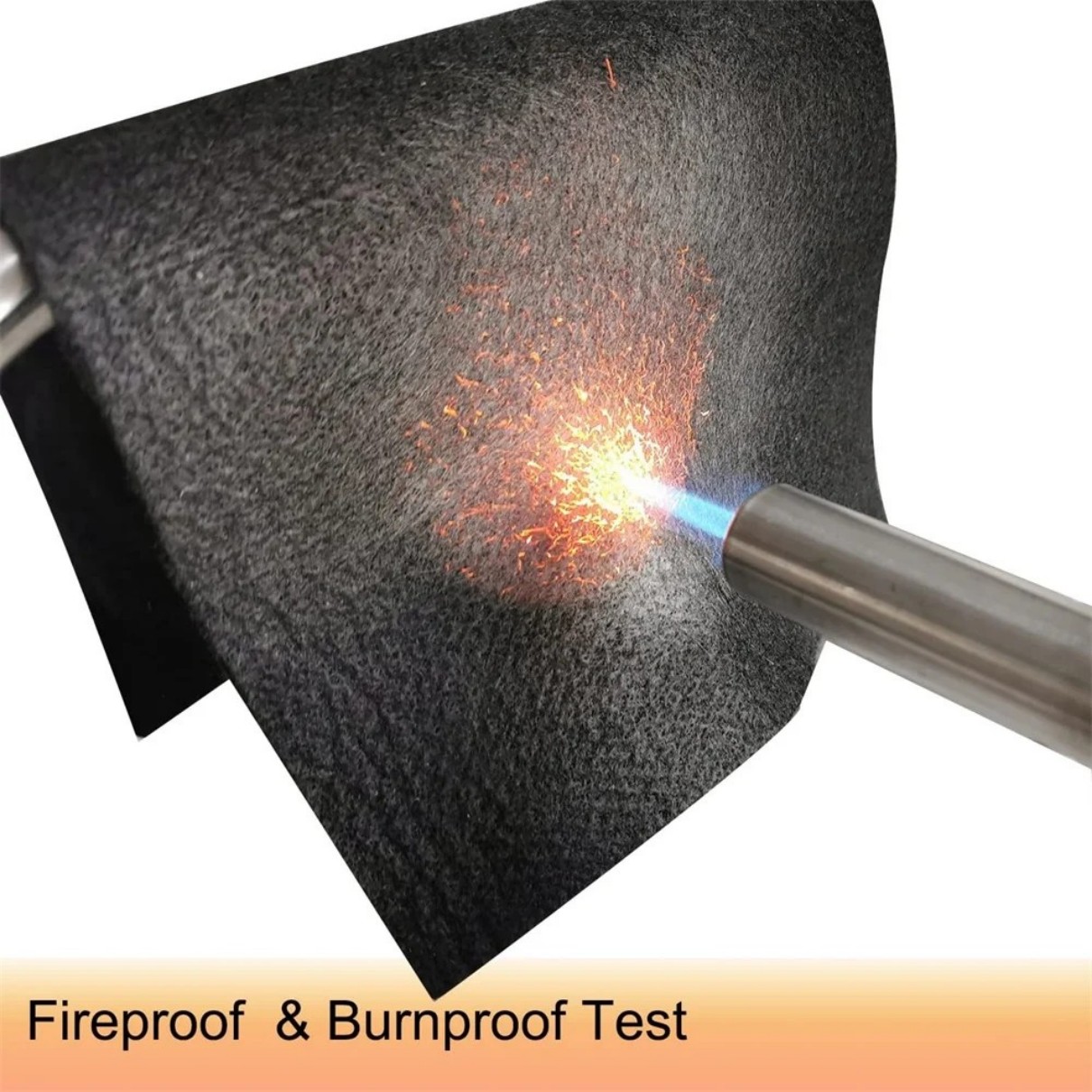
Welding fire blankets are heat-resistant fabrics designed to contain sparks, slag, and molten metal during welding, cutting, and grinding operations. Unlike regular fire blankets used in kitchens, welding blankets are made from specialized materials that withstand extreme temperatures up to 1,800°F (982°C).
These safety tools serve multiple purposes:
- Protecting nearby flammable materials from ignition
- Containing sparks and spatter within the work area
- Providing a safe surface for hot metal to cool
- Shielding workers from radiant heat
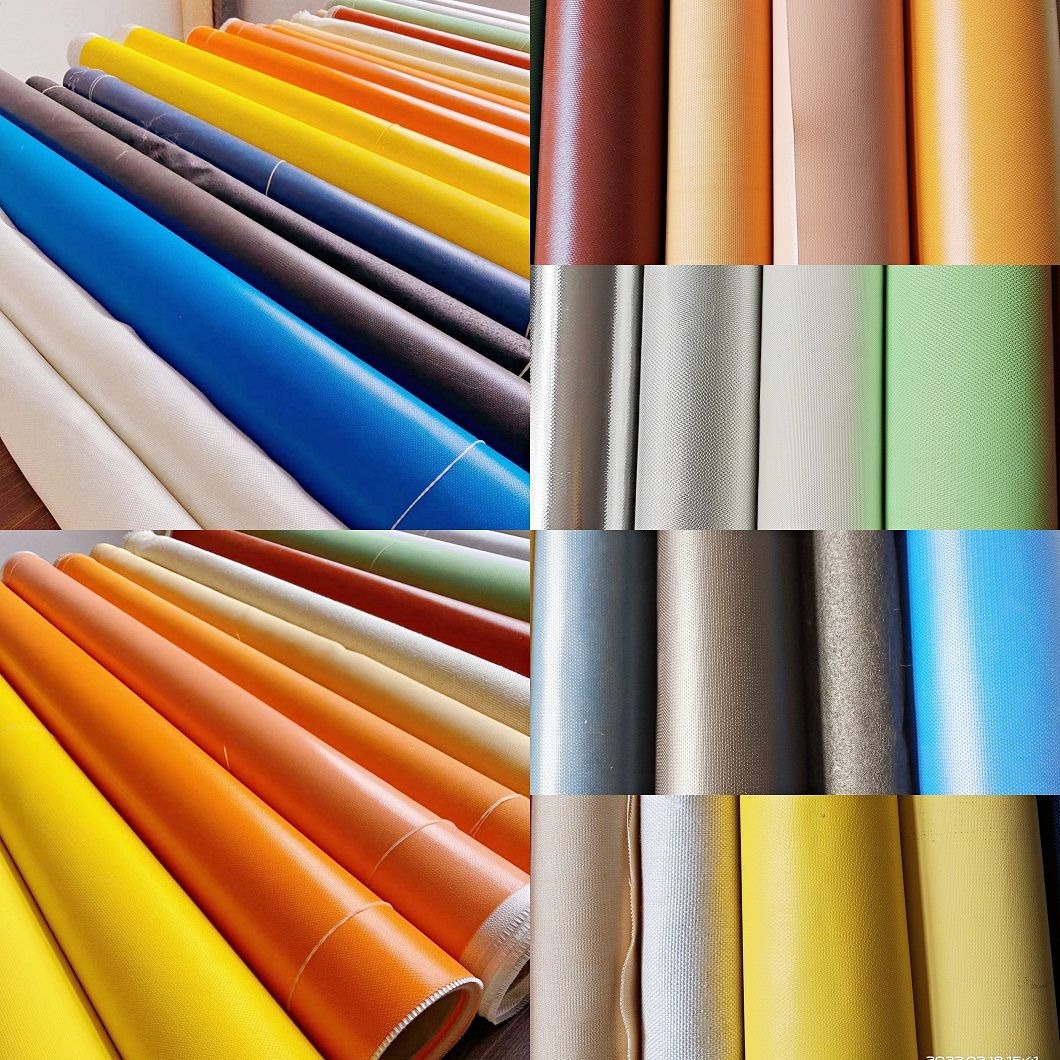
Key Materials in Welding Fire Blankets
Quality welding fire blankets use one of these three primary materials:
Fiberglass:The most common choice, offering good heat resistance (up to 1,000°F/538°C) at an affordable price. Fiberglass welding blankets are lightweight and flexible but can degrade with prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Silica:Withstands temperatures up to 1,800°F (982°C) and provides excellent protection against molten metal splash. Silica welding blankets are more durable than fiberglass but also more expensive.

Ceramic Fiber:The premium option for extreme heat applications (up to 2,300°F/1,260°C). These welding fire blankets offer superior protection but are more fragile and require careful handling.
Proper Usage of Welding Fire Blankets
To maximize safety and effectiveness:
- Cover all flammable materials within 35 feet of your welding area
- Overlap multiple blankets by at least 6 inches when covering large areas
- Secure blankets with non-flammable weights or clips to prevent movement
- Inspect for damage before each use - replace if you find holes or excessive wear
- Never use welding blankets as personal protective equipment (PPE) - they're for area protection only
Maintenance and Care
Proper care extends your welding fire blanket's lifespan:
- Shake out debris after each use
- Store flat or rolled - never fold, as this weakens fibers
- Clean with compressed air or gentle brushing - avoid water which can damage fibers
- Replace immediately if blanket becomes stiff, brittle, or develops holes
Choosing the Right Welding Fire Blanket
Consider these factors when selecting:
- Temperature rating:Match to your welding process (MIG/TIG welding typically needs higher ratings than soldering)
- Size:Measure your work area and add 20% coverage for safety
- Material:Fiberglass for general use, silica or ceramic for high-heat applications
- Thickness:Thicker blankets (1/4" or more) offer better protection but are less flexible
- Certifications:Look for NFPA 51B or OSHA compliance

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced welders sometimes make these errors with welding fire blankets:
- Using damaged blankets (compromises protection)
- Placing blankets directly on hot surfaces (use stands or spacers)
- Reusing blankets that have absorbed oils or chemicals (increased flammability risk)
- Assuming one blanket fits all applications (different jobs require different protection levels)
Beyond Welding: Other Uses
While designed for welding, these versatile blankets also work well for:
- Foundry work and metal casting
- Furnace maintenance
- Fireplace protection during chimney cleaning
- Emergency fire containment (though not a substitute for proper fire extinguishers)
Remember: Welding fire blankets are your first line of defense against workplace fires. Investing in quality blankets and using them properly significantly reduces fire risks during hot work operations.
For optimal safety, combine welding fire blankets with other protective measures like fire extinguishers, spark guards, and proper ventilation. Always follow your workplace's specific safety protocols for hot work operations.