Fire and Welding Blankets: Essential Safety Tools for Heat Protection
Fire and welding blankets are crucial safety tools that protect against heat, sparks, and flames. This guide explains their materials, uses, selection criteria, and proper handling to maximize workplace safety.
What Are Fire and Welding Blankets?
Fire and welding blankets are heat-resistant fabrics designed to smother fires, protect surfaces, and shield workers from thermal hazards. While similar in purpose, welding blankets typically offer higher temperature resistance than standard fire blankets.
Key Materials and Construction
These blankets come in different materials for various applications:
- Fiberglass:Most common, withstands temperatures up to 1000°F (538°C)
- Silica:Handles up to 1800°F (982°C), ideal for welding
- Carbon fiber:For extreme heat up to 3000°F (1649°C)
- Wool:Natural fiber option for lower-temperature applications
Quality blankets feature reinforced edges and sometimes aluminized coatings for extra reflectivity.
Primary Uses and Applications
You'll find fire and welding blankets useful for:
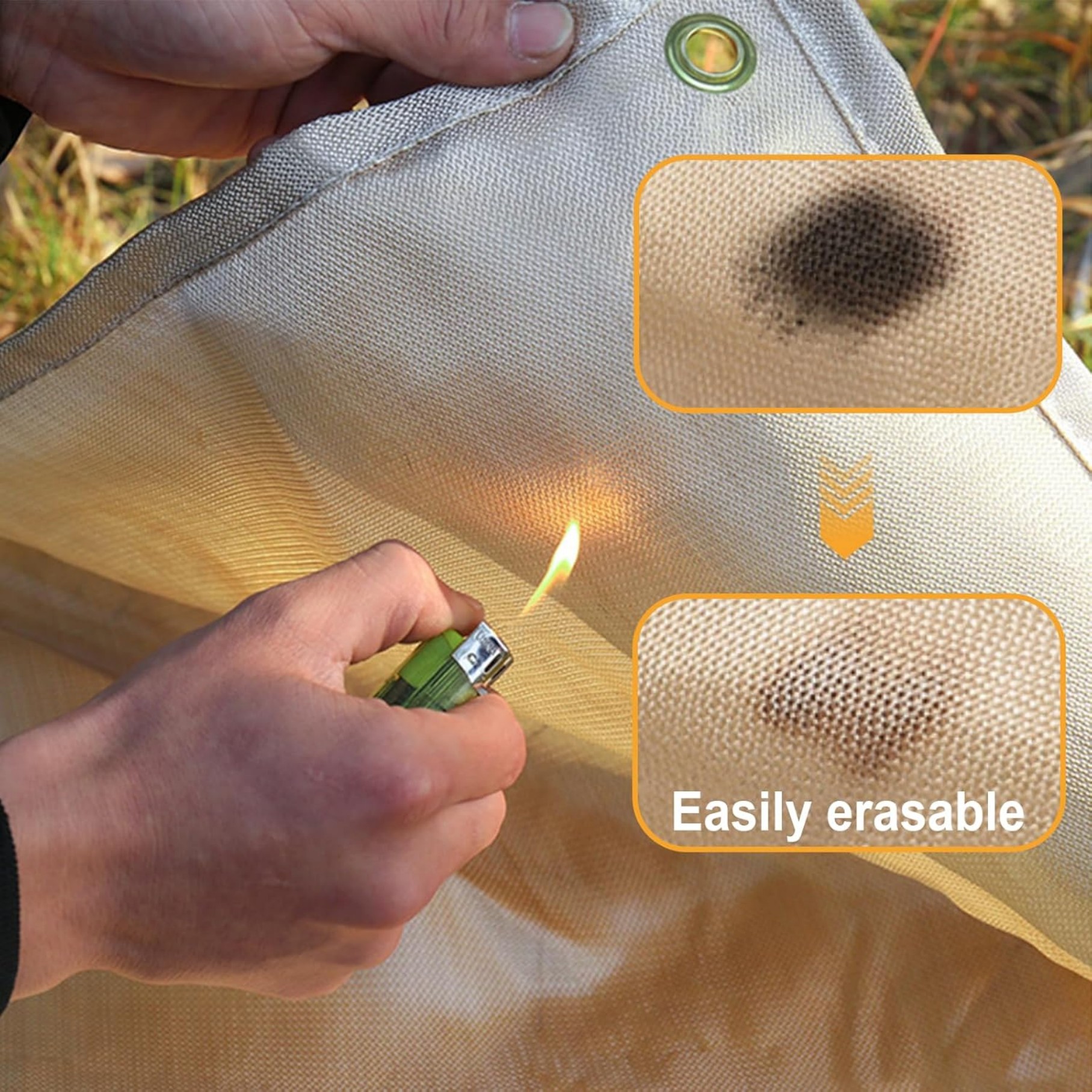
- Emergency fire suppression:Smother small fires by cutting off oxygen
- Welding protection:Shield nearby surfaces from sparks and slag
- Personal protection:Wrap around individuals during fire emergencies
- Equipment covering:Protect sensitive machinery from heat damage
- Containment:Control hot work areas in confined spaces
Choosing the Right Blanket
Select fire and welding blankets based on:
- Temperature rating:Must exceed your maximum expected heat exposure
- Size:Larger blankets cover more area but may be harder to handle
- Material:Match to your specific hazards (sparks, molten metal, etc.)
- Portability:Consider storage and quick-access needs
- Certifications:Look for NFPA, OSHA, or industry-specific approvals
Proper Use and Maintenance
To get the most from your fire and welding blankets:
- Store in easily accessible locations near potential hazard areas
- Inspect regularly for tears, holes, or contamination
- Replace if damaged or after single use in fire emergencies
- Clean according to manufacturer instructions (usually shaking or gentle brushing)
- Train all personnel on proper deployment techniques
Never use water to extinguish blanket-covered fires as this may cause steam burns.

Safety Limitations
While invaluable, fire and welding blankets have limits:
- Not effective against large or chemical fires
- Can degrade over time with repeated exposure to high heat
- Require proper technique to avoid burns during application
- Don't provide respiratory protection in smoke-filled areas
Industry-Specific Applications
Different sectors use these blankets uniquely:
Construction:Protect wooden structures during welding operations
Manufacturing:Cover flammable materials near production lines
Automotive:Shield vehicle interiors during repair work
Marine:Essential for confined space hot work on ships
Laboratories:Contain small chemical fires safely
Conclusion
Fire and welding blankets are simple yet vital safety tools that prevent injuries and property damage. By understanding their proper selection, use, and maintenance, you can significantly improve workplace safety during hot work operations and fire emergencies.